- Solutions
- ShieldVision™
- By Use Case
- Industries
- SOC
- Visibility Triad
- Knowledge Center
- Partners
- Company
- Talk to an Expert
Threat Summary:
On September 11th, 2023, MGM Resorts suffered a crippling ransomware attack that resulted in 10 days of computer system downtime as well as an estimated overall loss of $80,000,000. The threat actor, dubbed Scattered Spider, is claiming ownership of this hack and alleges to have ties with the infamous ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware gang. In this threat brief we will detail the events that occurred from initial access to recovery of MGM’s systems, common TTPs observed from this threat actor and other affiliated groups, as well as review detection, prevention, and mitigation options that would have been crucial to MGM’s security in all stages of this attack.
Lumifi’s Analysis:
To fully understand this attack, we need to look back into the previous operations of this threat actor. Throughout 2022 and early 2023, this threat actor primarily targeted systems that would provide access to SIM swapping attacks, as well as performing privilege escalation through BYOVD attacks (CVE-2015-2291.) Performing a SIM swapping attack would allow the threat actor to gain access to any data sent to the victim’s phone number. By establishing pre-requisite access to these systems, the threat actor already had the infrastructure in place to receive MFA codes sent to the target’s phone number via SMS, as well as masquerade as the target when making outbound calls.
Fast forward to September 8th, 2023; The threat actor places a call to MGM Resort’s internal IT helpdesk impersonating a legitimate employee (whose information was likely located on social media such as LinkedIn or Facebook.) Once connected with a helpdesk agent, a password reset is requested and processed for the impersonated user account, with MFA being bypassed via SIM swapping, resulting in initial access for the attacker. Currently, this is all the information that has been confirmed in regard to the MGM compromise, however, the rest of the attack chain is predictable based on previous activity from this threat actor.
After gaining initial access, this threat actor has been observed using a VPN or local proxy to geolocate to the local area where the attack is occurring, in an attempt to blend in with the regular traffic and evade detection. Then the threat actor installs legitimate remote access software such as TeamViewer or AnyDesk as a persistence mechanism into the compromised environment. In the past, this threat actor has also been observed creating publicly accessible VMs in the victim’s cloud environment as a means of persistence.
Once persistence is established, this threat actor will spend significant time reviewing internal documentation, resources, and chat logs in an attempt to help with privilege escalation and long-term persistence. Additionally, this threat actor often achieves privilege escalation by targeting password managers and PAM systems as well as utilizing tools such as Mimikatz, Trufflehog and GitGuardian. After gaining escalated privileges, this group will begin to move laterally in the environment and performing internal reconnaissance to identify critical infrastructure.
After successfully gaining access to critical infrastructure, this threat actor will begin performing exfiltration of sensitive data via tools like RClone and DropBox. After the desired data is exfiltrated, the Volume Shadow Copy service is stopped and all shadow copies are deleted or corrupted. Finally, this threat actor will deploy the ALPHV ransomware variant resulting in the encryption of critical systems and leave threatening notes in text files, contact executives via email and text, as well as infiltrating communication channels used to respond to incidents.
Lumifi’s Current Coverage and Mitigation Recommendations:
The Scattered Spider APT is also known to have overlap and ties to a number of other ransomware groups and APTs as demonstrated via the below screen capture from a Mandiant threat researcher at Sleuthcon 2023. Considering the wide array of connections and overlap between these groups, there is also a high likelihood of the tactics observed by one group being utilized by others.
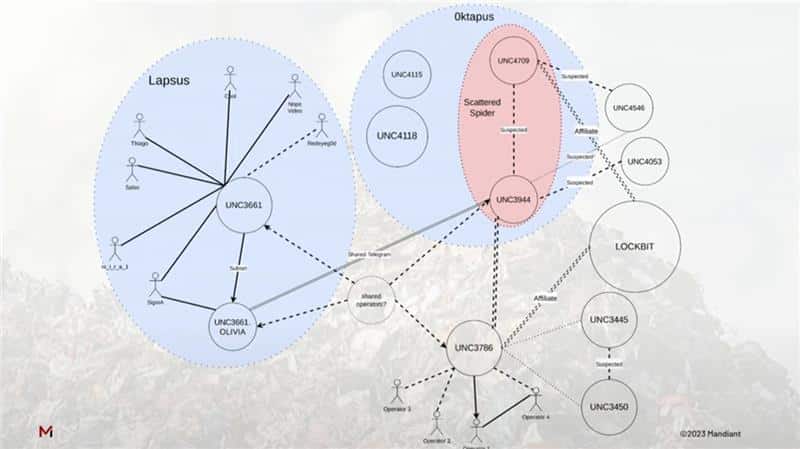
Link between Threat Actors (Lapsus, Oktapus, Scattered Spider)
Source: Jake Nicastro, Mandiant, at Sleuthcon 2023
Mitigation for the threats posed by this APT would include:
Subscribe to Lumifi's Daily Cybersecurity News Curated by a CISO
Date: 01.28 | Time: 1:00 PM MT